People tend to view the gut as simply a digestive organ. However, research has shown that the gut is much more complicated-and surprisingly connected to the brain. Many people are not aware that the gut can actually influence our thoughts, moods, and behaviour.
The gut-brain connection is not merely speculation. Research backs up the idea that the digestive system is directly linked to our mental well-being, which in turn helps explain why anxiety, stress, and depression often co-occur with digestive disorders. In this article, we will discuss the relationship between your digestive system and Gut Health and how taking care of your gut can help foster a more relaxed and clear mind.
What Is the Gut-Brain Connection?
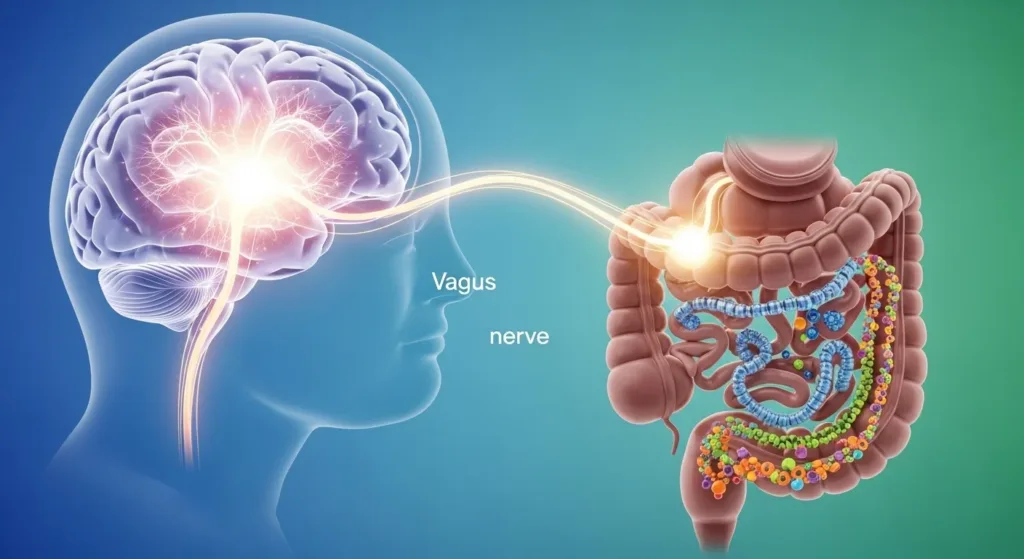
Your gut and your brain are always communicating with one another through a mechanism called the gut-brain axis. The gut-brain axis is a two-way system containing nerves, chemicals, and hormones that allow communication between your gut and your brain.
When things are awry in your body, those two-way messages are affected, causing damage to the gut-brain axis and potentially affecting digestion, inflammation, mental health, and, likewise, further affecting mood and focus.
How the Gut Communicates with the Brain?
Let’s look at the primary ways your gut and brain communicate:
1. The Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve is an extensive nerve that connects the brainstorm with the abdomen, which is part of the parasympathetic nervous system. The vagus nerve connects the brain’s neural signals to the gut. Since the vagus nerve has a two-way street, if the gut is irritated or inflamed, then the signals generated by the gut travel up the vagus nerve and can affect emotional states.
2. Neurotransmitters Generated in the Gut
The gut generates neurotransmitters, which are the brain’s chemical messengers. Serotonin is an example of a neurotransmitter that functions in the brain. Interestingly, almost 90% of serotonin, which regulates mood and sleep, comes from the gut.
3. The Immune System and Inflammation
A major part of the immune system exists in your gut. When you’re experiencing gut dysfunction, it can trigger low-grade inflammation that researchers have linked to symptoms of both anxiety and depression.
4. Brunner’s Glands
Brunner’s glands play an important role in the gut-brain relation, as these branched tubules in the small intestine secrete mucus to protect the lining during times of stress. What is really remarkable is that they respond to signals from brain parts that are involved in emotional control.
What Happens When Your Gut Is Out of Balance?
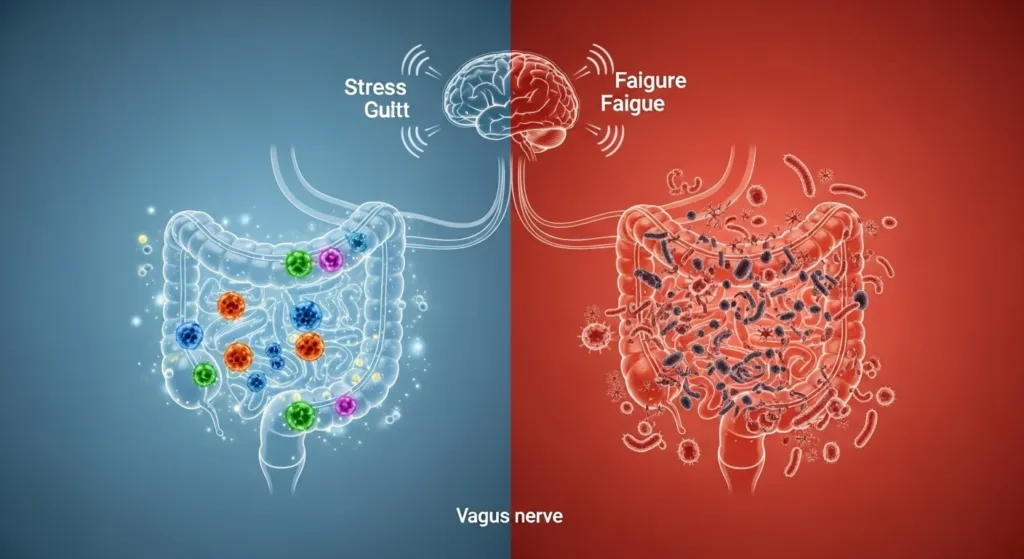
Your brain can potentially feel the effects when the balance of good bacteria and bad bacteria in your gut is disrupted (a condition called dysbiosis).
Here are some common effects poor gut health can have on the mind:
1. Irritability and Mood Swings
A disrupted gut can diminish the amount of calming neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, which may lead to irritability or sadness.
2. Stress and Anxiety
A disruption of gut bacteria can amplify your levels of stress response, resulting in increased feelings of anxiety, feeling overwhelmed, or being on edge.
3. Memory Problems or Noisy Brain
It’s common for people who have problems with their digestion or digestive system to also have difficulty paying attention or remembering things. It can often be the result of inflammation or poor nutrient absorption due to gut problems.
The Gut-Brain Connection
One of the most interesting things about the gut-brain axis is that it’s bidirectional. This means that not only can your gut affect your brain, but your mental state can also impact your gut health.
Mental Health Affects the Gut
Stress, trauma, and anxiety can all lead to gut problems like bloating, cramps, constipation, or diarrhea. This is why people under stress often develop IBS or other digestive disorders.
Gut Health Affects Mental Health
On the other hand, improving your gut can often lead to better mood, clearer thinking, and less anxiety. A balanced microbiome (gut bacteria) helps produce brain-healthy chemicals and reduce inflammation.
How to Improve Gut Health and Support Your Mind

Taking care of your gut and your mind can be simple and practical. Here are a few easy tips you can try:
1. Eat Whole, Unprocessed Foods
Eating as many fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and healthy fats nourishes your gut’s good bacteria.
2. Eat Fermented Foods
Fermented foods are a source of natural probiotics and include yogurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso.
3. Eat Prebiotic Foods
Prebiotics are a unique type of fiber that acts as a food source for gut-friendly bacteria, and are found in foods such as garlic, onions, bananas, and oats.
4. Naturally manage Stress
Stress can really disrupt your gut. Taking a mindfulness approach like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or journaling can reduce the effects of stress on your gut.
5. Sleep and Movement Can Benefit Gut Health
Sleep and movement are important to gut health, but they’re also the key pieces to regulating our mood.
6. Seek Help
If the symptoms are persisting and interfering with your life, it’s time to reach out to your practitioner. Sometimes it will take a registered dietitian, a gastroenterologist, or a therapist.
Final Thoughts
The relationship between gut health and mental health is real, and it’s important. Your gut processes what you eat and how you feel.
When you create a focus on your digestive wellness, you may be able to diminish anxiety, lessen brain fog, and feel emotionally more balanced. It is a reminder of how your body is connected to your mind and taking care of one helps the other.
FAQ
1. Can changing my diet impact my mental health?
Absolutely. Diets that are high in fiber and fermented foods have been connected to higher moods and lower anxiety.
2. How to calm the gut brain?
You should add more whole, unprocessed foods, fruits, veggies, and fermented foods in your meal. Daily movement, such as walking, slow deep breathing, probiotics, and fiber to both soothe your gut lining as well as relieve any brain-gut tension.
3. Should I take probiotics for mental health?
Yes, taking probiotics may help you maintain mental health. They can help promote a balanced gut microbiome which plays a significant role in mood, focus and stress. Since most of your serotonin (the “feel-good” chemical) is produced in your gut, maintaining good gut health will translate to a more relaxed mind and better mental clarity.
4. How can I improve my gut health to reduce anxiety?
Limit processed foods and sugars, drink more water, and eat more fiber and fermented foods. Get enough sleep, move your body frequently, take probiotics when you can, and use methods to reduce stress like writing down your thoughts or deep breathing.
5. Why is the gut health called second brain?
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is a network of nerves in your gut which functions on its own but stays in communication with the brain. Your gut produces chemicals that can influence your mood, like serotonin. Because of this strong connection, your gut can have a significant effect on how you feel. That’s why it’s sometimes called your “second brain.”

